The post The Science Behind UV Flashlight for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>What is Resin Curing?
Resin curing refers to the process in which liquid resin is transformed into a hard, solid form. This transformation happens when a chemical reaction is triggered by UV light or heat, depending on the type of resin being used. UV resin curing is particularly popular because it offers quick and precise curing, which makes it ideal for applications that require detailed work.
- Photoinitiators: Special chemicals in UV resin that react when exposed to UV light, causing the resin to polymerize and harden.
- Polymerization: The process in which molecules in the resin bond together to form a solid structure.
How Does UV Flashlight Cure Resin?

Step 1: Exposure to UV Light
When UV resin is exposed to ultraviolet light, it reacts with photoinitiators within the resin. This initiates the polymerization process, where the molecules in the resin start bonding together to form a hardened material.
| Photoinitiator | Reaction Under UV Light |
|---|---|
| Benzoin ethers | Causes rapid curing, common in many UV resins. |
| Camphorquinone | Often used in dental applications, reacts with light to harden the resin. |
| Thioxanthone | Used in inks and coatings, leads to hardening when exposed to UV. |
UV light wavelength: For the resin curing process, the wavelength of the UV light typically ranges between 365nm and 405nm. Different wavelengths react with different photoinitiators, which makes selecting the right UV flashlight essential for optimal curing.
Step 2: Polymerization and Hardening
Once the resin is exposed to UV light, the photoinitiators trigger polymerization. This process causes the liquid resin to become hard and durable.
| Wavelength | Resin Curing Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| 365nm | Ideal for deeper curing, suitable for thick resins and professional applications. |
| 405nm | Good for surface curing and faster results, commonly used for thin layers of resin. |
Key Factors in UV Resin Curing with Flashlights
1. Wavelength of the UV Flashlight
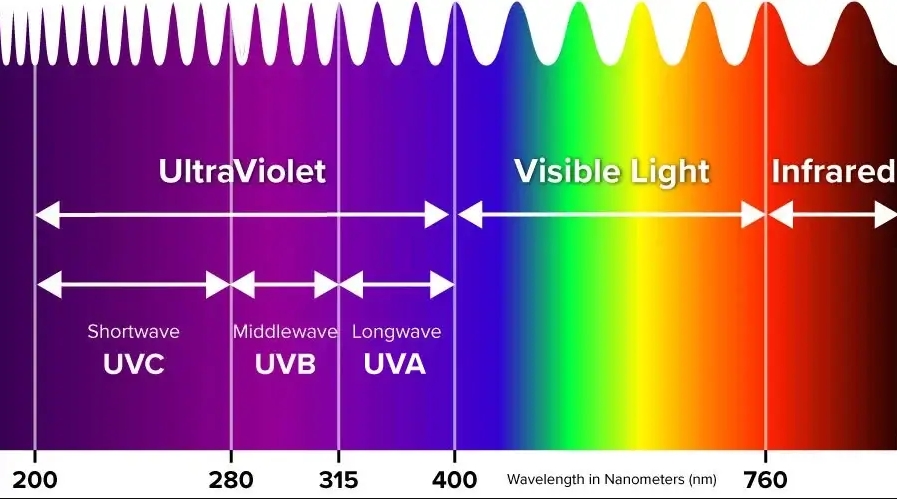
The wavelength of the UV flashlight plays a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of resin curing. Flashlights that emit a wavelength of 365nm provide a deeper and more intense curing effect, which is ideal for thick resin layers. 405nm wavelengths are effective for surface curing and are typically used for smaller or thinner resin projects.
- 365nm UV light: Best for curing deep layers and professional-grade resin applications. It provides better penetration into the resin.
- 405nm UV light: Typically used for curing thin layers of resin faster, suitable for DIY projects and small crafts.
| Wavelength | Depth of Curing | Best for |
|---|---|---|
| 365nm | Deeper penetration and longer curing time. | Professional-grade resin, deep applications. |
| 405nm | Surface curing with faster results. | Small-scale applications, quick-drying projects. |
2. UV Flashlight Power (Wattage)
The power output of a UV flashlight is another important factor. Higher wattage results in stronger UV light output, leading to faster curing. However, it is essential to balance power with resin thickness, as very high wattage can cause uneven curing if the resin is too thick.
| Wattage | Effect on Curing |
|---|---|
| 3W-5W | Suitable for general resin curing. |
| 5W-10W | Provides faster curing, ideal for professional use. |
| 10W+ | High power for quick curing of thicker resin layers. |
3. Exposure Time
The curing time depends on several factors, including the type of resin, the UV light intensity, and the resin’s thickness. Generally, thicker resins require longer exposure to UV light. Most UV resins will cure within a few minutes to an hour, depending on these factors.
| Resin Thickness | Exposure Time (at 365nm) |
|---|---|
| Thin Layer | 1-3 minutes |
| Medium Layer | 5-10 minutes |
| Thick Layer | 20-60 minutes |
Advantages of Using UV Flashlight for Resin Curing
- Speed: UV curing can occur in just a few minutes, unlike traditional curing methods that may take hours.
- Precision: With a UV flashlight, you can focus light on specific areas, ensuring precise curing without affecting surrounding surfaces.
- Convenience: Portable and easy to use, making it ideal for small-scale or DIY projects.
- Energy Efficient: UV flashlights consume less power compared to traditional curing ovens, which is especially beneficial for smaller workshops.
How to Choose the Right UV Flashlight for Resin Curing
When selecting a UV flashlight for resin curing, here are some factors to consider:
| Factor | What to Consider |
|---|---|
| Wavelength | Choose 365nm for deeper curing and 405nm for faster surface curing. |
| Power | Higher wattage (5W+) for quicker curing, lower wattage (3W) for precision. |
| Portability | Choose a compact, rechargeable flashlight for DIY or fieldwork. |
| Durability | Look for a flashlight with an aluminum body or impact-resistant design. |
Recommended UV Flashlight for Resin Curing: TANK007 K9A5
For efficient and high-quality resin curing, the TANK007 K9A5 UV Flashlight is a top choice. This flashlight offers:
- 365nm Wavelength: Provides optimal curing depth for a variety of resin types.
- Powerful 5W LED: Ensures fast and even curing for thick resin layers.
- Rechargeable Battery: Convenient and cost-effective, with long-lasting performance.
- Durable and Compact: Perfect for both professionals and hobbyists.
Conclusion
UV flashlights play a vital role in the resin curing process, enabling rapid and precise curing for a wide range of applications. By understanding the science behind UV curing, including the importance of wavelength, power, and exposure time, you can select the right flashlight for your resin projects.
The post The Science Behind UV Flashlight for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post Benefits of Using UV Flashlights for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>Why Use UV Flashlights for Resin Curing?
UV flashlights use ultraviolet light to cure UV-sensitive resin quickly and precisely. This process involves activating photoinitiators within the resin to harden it, offering a rapid and controlled method for small-scale or intricate projects.
Key Benefits of UV Flashlights for Resin Curing

1. Speed and Efficiency
- Rapid Curing: UV flashlights cure resin within seconds to minutes, depending on the layer thickness and resin type.
- Layered Application: Thin layers can be cured successively for a smooth, bubble-free finish.
2. Precision and Control
- Focused Beam: Allows for curing specific areas without affecting surrounding parts of the project.
- Adjustable Zoom: Many UV flashlights feature zoomable lenses for greater accuracy.
3. Portability
- Compact Design: Easy to carry and use anywhere, whether in a studio or on-site.
- Battery Operated: No need for a direct power supply, making it perfect for outdoor or mobile setups.
4. Cost-Effective Solution
- Affordable Entry Point: UV flashlights are generally less expensive than larger UV lamps.
- Durability: High-quality UV flashlights, like the Tank007 AA02, offer long-lasting performance.
5. Versatility
- Multiple Applications: Beyond resin curing, UV flashlights can be used for tasks such as detecting counterfeit currency, scorpion hunting, or mineral inspections.
Comparing UV Flashlights to UV Lamps

| Feature | UV Flashlight | UV Lamp |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Compact and portable. | Bulky and stationary. |
| Beam Control | Focused beam for precise curing. | Wider coverage, less precise. |
| Curing Speed | Slightly slower for large areas. | Faster for batch or large-scale projects. |
| Cost | Generally more affordable. | Higher initial investment. |
| Best Use Case | Small, intricate projects and portable needs. | Professional, large-scale, or batch projects. |
How to Maximize the Benefits of UV Flashlights
Choose the Right Wavelength
- 365nm: Ideal for professional-grade resin projects due to its pure UV output.
- 395nm: Suitable for hobbyist projects but may require longer curing times.
Use High-Quality Tools
The Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight is a top choice for resin curing with:
- 365nm wavelength for precise curing.
- 3W power output for fast and efficient results.
- Durable design for long-term use.
Follow Best Practices
- Cure in Layers: For thicker pieces, cure the resin in multiple thin layers to ensure even hardening.
- Avoid Overexposure: Excessive UV light can cause resin to yellow or crack.
- Use Safety Gear: Protect your eyes and skin from UV exposure with goggles and gloves.
Case Study: UV Flashlights in Action

Scenario: Crafting Resin Jewelry
A jewelry artist needed precise curing for intricate designs in resin pendants. Using the Tank007 AA02 UV flashlight, they achieved:
- Rapid Curing: Each pendant layer cured in under 30 seconds.
- Perfect Finish: Smooth, bubble-free surfaces due to layered curing.
- Increased Productivity: Ability to complete multiple pieces in a single session.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I use a 395nm UV flashlight for resin curing?
A: Yes, but 395nm flashlights may require longer exposure times and may not cure all resin types effectively.
Q: How do I know if my resin is UV-sensitive?
A: Check the manufacturer’s label; UV-sensitive resins are specifically designed to cure with ultraviolet light.
Q: Is a higher wattage always better?
A: Higher wattage often means faster curing, but ensure compatibility with your resin type to avoid overheating or overcuring.
Conclusion
UV flashlights are an indispensable tool for resin curing, offering unmatched speed, precision, and versatility. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, investing in a high-quality UV flashlight.
The post Benefits of Using UV Flashlights for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post UV Lights for Resin Curing: 365nm vs 395nm Which is Better? appeared first on Tank007.
]]>Understanding UV Light and Resin Curing

UV light plays a key role in curing resin by initiating a photochemical reaction that hardens the material. The effectiveness of this process largely depends on the wavelength of the UV light used.
- 365nm UV light: Falls in the UVA spectrum, producing deeper and more precise curing.
- 395nm UV light: Also in the UVA spectrum but closer to visible light, offering slightly broader usability but less depth in curing.
Both wavelengths can cure resin, but choosing the right one depends on your project’s requirements.
Key Differences Between 365nm and 395nm UV Lights
| Feature | 365nm UV Light | 395nm UV Light |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 365 nanometers | 395 nanometers |
| Curing Depth | Deeper curing, ideal for thicker resins | Shallower curing, better for surface layers |
| Resin Compatibility | Works with most UV-curable resins | Works with resins less sensitive to UV light |
| Light Visibility | Low visibility (less visible to the naked eye) | High visibility (purple hue to the naked eye) |
| Heat Generation | Minimal heat during operation | Generates more heat |
| Power Consumption | Slightly higher due to precision | Lower power consumption |
| Applications | Professional-grade applications | General-purpose and hobbyist use |
| Cost | Typically more expensive | More affordable |
Benefits of 365nm UV Lights for Resin Curing
- High Precision: The shorter wavelength ensures more accurate and uniform curing, even in thicker resin layers.
- Deeper Penetration: Suitable for high-quality or professional resin projects.
- Minimal Yellowing: Prevents discoloration in clear resins, ensuring a clean finish.
Recommended Product: Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight
- Features: High-power 365nm UV LED, professional-grade optical design, uniform light projection.
- Ideal For: Precision resin curing, mineral identification, and other professional applications.
- Learn More About AA02 Here
Benefits of 395nm UV Lights for Resin Curing

- Budget-Friendly: More affordable and widely available.
- Visible Light: Easier to see where the UV light is being applied.
- Good for Surface Curing: Works well for thin resin layers or quick fixes.
Choosing the Right UV Light for Your Project
When deciding between 365nm and 395nm UV lights, consider the following factors:
- Project Type: For professional applications or intricate designs, opt for a 365nm UV light. For general crafting or hobby projects, a 395nm UV light may suffice.
- Resin Thickness: Thicker resins benefit from the deeper penetration of 365nm UV lights.
- Budget: 395nm UV lights are a more economical choice for beginners or occasional use.
Practical Tips for Using UV Lights in Resin Curing

- Work in a Dark Environment: This minimizes interference from ambient light, ensuring optimal curing.
- Maintain Proper Distance: Keep the UV flashlight 2–5 inches from the resin surface for best results.
- Curing Time: Follow the resin manufacturer’s guidelines for exposure time, adjusting based on the UV light wavelength.
- Safety Precautions: Always wear UV-blocking glasses to protect your eyes from prolonged exposure.
Conclusion
Both 365nm and 395nm UV lights have their place in resin curing, but the best choice depends on your specific needs. If you’re aiming for professional-grade results or working with thicker resin layers, a 365nm UV light like the Tank007 AA02 is the ideal option. For general-purpose applications or budget-friendly solutions, 395nm UV lights can be effective.
By understanding the specifications and benefits of each wavelength, you can make an informed decision and achieve the best possible results in your resin curing projects. For premium-quality UV flashlights, explore our range at Tank007.
The post UV Lights for Resin Curing: 365nm vs 395nm Which is Better? appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post How UV Light Reacts with Resin During Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>UV curing resin is widely used in industries such as electronics, coatings, adhesives, and 3D printing. UV light plays a critical role in initiating the chemical reactions necessary for resin hardening, offering a fast and efficient curing process.
1. The Science Behind UV Resin Curing
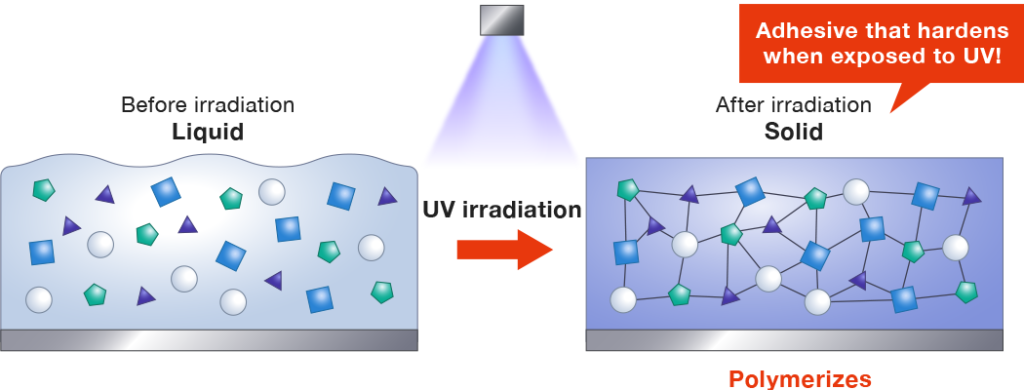
UV resin curing is a photochemical process where ultraviolet (UV) light initiates polymerization, transforming liquid resin into a solid state.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Photoinitiator | Absorbs UV light and breaks down into reactive radicals. |
| Oligomers and Monomers | Serve as the primary building blocks of the cured polymer. |
| Additives | Improve the physical and chemical properties of the cured resin. |
Chemical Reaction:
- When UV light hits the photoinitiators in the resin, it breaks their chemical bonds, releasing free radicals.
- These radicals trigger cross-linking between monomers and oligomers, forming a durable polymer network.
2. Key Factors Influencing UV Resin Curing
Several factors affect the efficiency and quality of UV curing:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Curing |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | UV light wavelength (typically 365nm or 405nm) must match the photoinitiator’s absorption spectrum. | Proper wavelength ensures complete curing. |
| Light Intensity | The power of the UV light source. | Higher intensity accelerates curing but may cause overheating. |
| Exposure Time | Duration of UV light exposure. | Insufficient time leads to incomplete curing. |
| Resin Thickness | Thickness of the resin layer. | Thicker layers require longer curing times. |
3. Step-by-Step UV Resin Curing Process

- Preparation: Ensure the resin is evenly applied on the desired surface.
- Positioning: Place the UV light source at the recommended distance from the resin surface.
- Exposure: Expose the resin to UV light for the specified duration.
- Cooling: Allow the cured resin to cool to prevent warping or cracking.
- Inspection: Check for uncured spots and re-expose if necessary.
| Step | Key Action | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Proper resin application | Ensures uniform curing. |
| 2 | Correct UV light positioning | Prevents uneven curing. |
| 3 | Adequate exposure time | Achieves full polymerization. |
| 4 | Cooling phase | Reduces thermal stress. |
| 5 | Final inspection | Ensures product quality. |
4. Comparison: UV Resin Curing vs. Traditional Heat Curing
| Criteria | UV Resin Curing | Traditional Heat Curing |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Time | Fast (seconds to minutes) | Slow (hours) |
| Energy Consumption | Lower | Higher |
| Precision | High precision for thin layers | Less precise for detailed work |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced emissions | Higher emissions |
| Application Scope | Ideal for electronics, coatings, and adhesives | Better for bulk curing processes |
Conclusion: UV curing is significantly faster, more energy-efficient, and more precise compared to traditional heat curing methods.
5. Common Issues and Troubleshooting During UV Resin Curing
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Sticky Surface | Insufficient UV exposure or incorrect wavelength. | Increase exposure time or use the correct UV light source. |
| Uneven Curing | Improper light positioning or resin application. | Adjust light placement and ensure even resin application. |
| Overheating | Excessive light intensity or prolonged exposure. | Reduce UV light intensity or limit exposure duration. |
6. Safety Precautions When Using UV Light for Resin Curing
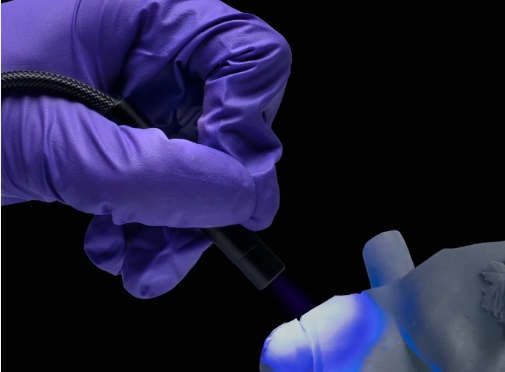
- Wear UV-protective glasses and gloves.
- Avoid direct skin or eye exposure to UV light.
- Use proper ventilation to prevent inhalation of resin fumes.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for resin and UV equipment.
7. Final Thoughts
Understanding how UV light interacts with resin during curing is essential for achieving consistent, high-quality results. By controlling factors like wavelength, intensity, and exposure time, you can optimize the curing process for a variety of applications. Whether you are working on industrial projects or small DIY crafts, mastering UV resin curing will ensure professional outcomes.
By implementing these insights, businesses and hobbyists can make the most of UV light technology in resin curing processes.
The post How UV Light Reacts with Resin During Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>