The post Can UV Flashlights Cure Resin? A Complete Guide appeared first on Tank007.
]]>In this guide, we’ll explore how UV flashlights can be used to cure resin, what makes them effective, and which flashlights are best suited for this task.
What is Resin Curing?
Resin curing is the process of hardening a liquid resin by exposing it to UV light. Many resins used in 3D printing or crafting (such as UV resin) require a specific wavelength of light to initiate the chemical reactions that harden the material. Curing is essential for turning the resin from a liquid to a solid, making it ideal for creating durable, high-precision objects.
How Does UV Light Cure Resin?
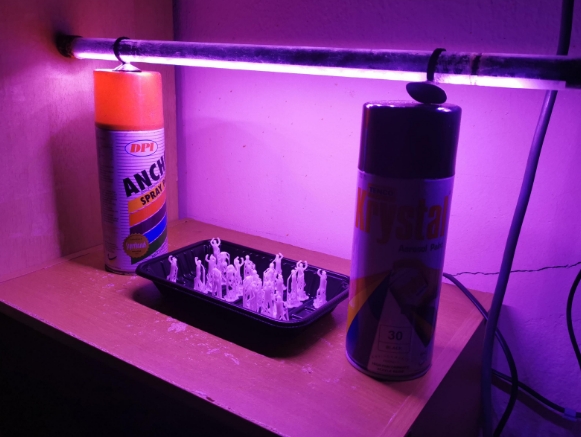

UV light, specifically UV light in the 365 nm to 405 nm wavelength range, is absorbed by the chemicals in the resin, causing them to harden. The UV light acts as a catalyst, triggering a photopolymerization process that solidifies the resin.
- 365 nm light is ideal for curing most UV resins as it activates the polymerization process more efficiently than higher wavelengths.
- 405 nm light can also work, but it may be slower or less effective for certain types of resin, especially those designed for 3D printing.
Can UV Flashlights Cure Resin?
Yes, UV flashlights can cure resin, but not all UV flashlights are suitable for this task. The effectiveness of the flashlight in curing resin depends on a few key factors:
- Wavelength: The flashlight must emit light in the correct UV spectrum, ideally 365 nm for optimal curing.
- Power Output: The intensity or power output of the UV flashlight is crucial. A low-power flashlight will not provide enough light to cure resin effectively. Typically, a UV flashlight with a 3W to 5W output is recommended for resin curing.
- Curing Time: Flashlights tend to cure resin more slowly compared to UV lamps designed for the purpose. Resin pieces exposed to UV flashlights may need to be exposed for a longer period.
Key Considerations When Choosing a UV Flashlight for Resin Curing
To choose the right UV flashlight for curing resin, consider the following factors:
| Factor | Why It Matters | What to Look For |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | Affects the efficiency of the curing process. | Look for flashlights that emit 365 nm UV light. |
| Power Output | Determines how quickly and effectively the flashlight can cure the resin. | Opt for flashlights with 3W to 5W power output. |
| Curing Area Size | The size of the resin piece being cured affects the amount of light needed. | A larger curing area requires a more powerful flashlight or a flashlight with adjustable focus. |
| Battery Life/Rechargeability | Long curing sessions require sufficient battery life. | Choose a flashlight with rechargeable batteries for long sessions or AA batteries for portability. |
| Build Quality | Durability is important if you’re using the flashlight frequently. | Ensure the flashlight is made of sturdy materials and is water-resistant for ease of use. |
| Beam Focus | Focused light allows for targeted curing of specific areas. | Look for flashlights with adjustable focus to tailor the beam for different resin pieces. |
Steps to Cure Resin with a UV Flashlight
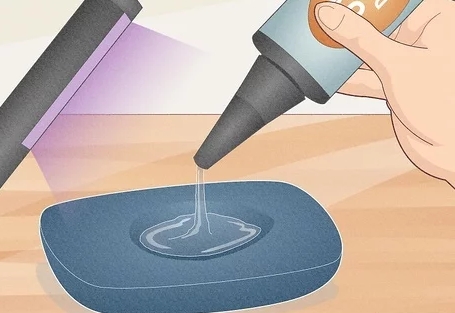
Here’s a step-by-step guide to curing resin with a UV flashlight:
- Prepare the Resin: After applying the resin to your project, ensure it’s evenly spread and in the desired shape.
- Choose the Right UV Flashlight: Make sure your UV flashlight has the proper wavelength (365 nm) and power output (3W to 5W).
- Position the Flashlight: Hold the UV flashlight about 2-6 inches above the resin. Ensure the beam is focused directly on the resin’s surface for even curing.
- Cure the Resin: Shine the flashlight on the resin. Depending on the resin’s thickness and the flashlight’s power, the curing process can take anywhere from 1 to 5 minutes for smaller objects, and longer for larger pieces.
- Check the Cured Resin: After the curing time has passed, check the resin to ensure it’s fully solidified. If necessary, cure it for additional time in small increments.
Best UV Flashlights for Resin Curing
Here’s a comparison of UV flashlights that are great for curing resin, along with a recommendation for the Tank007 K9A5 UV Flashlight.
| Model | Wavelength | Power Output | Battery Type | Curing Time | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tank007 K9A5 UV Flashlight | 365 nm | 3W | Rechargeable USB | 3-5 minutes (small objects) | High intensity, portable, adjustable beam, compact design. |
| Streamlight 51018 UV | 365 nm | 5W | AA Batteries | 5-10 minutes (larger objects) | Water-resistant, durable, professional-grade light output. |
| Nitecore EA41 UV | 365 nm | 5W | Rechargeable Li-ion | 4-6 minutes (depending on size) | Adjustable zoom, long battery life, rugged build. |
| Fenix UV-5 | 365 nm | 2W | Rechargeable Li-ion | 5-7 minutes (depending on size) | Compact, lightweight, energy-efficient. |
How Long Does It Take to Cure Resin with a UV Flashlight?
The time it takes to cure resin with a UV flashlight can vary based on the flashlight’s power output, the thickness of the resin, and the size of the resin piece. Typically:
- Thin layers of resin: 1-3 minutes of exposure.
- Thicker layers or larger objects: 5-10 minutes of exposure.
For large 3D printed objects, you may need to move the flashlight around the surface to ensure even curing, as UV flashlights have a smaller curing area compared to UV curing lamps.
Conclusion
Yes, UV flashlights can cure resin, but it’s essential to select the right flashlight for the job. Look for one with the correct 365 nm wavelength and a 3W to 5W power output to ensure effective and efficient curing. While a UV flashlight can cure resin, it may take a bit longer compared to dedicated UV lamps, and some resins may require more powerful light sources to cure properly.
If you’re just getting started with resin curing, the Tank007 K9A5 UV Flashlight is an excellent choice for both beginners and professionals, providing high performance, durability, and a 365 nm wavelength ideal for resin curing.
The post Can UV Flashlights Cure Resin? A Complete Guide appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post Best UV Flashlight for Resin Curing: A Detailed Guide appeared first on Tank007.
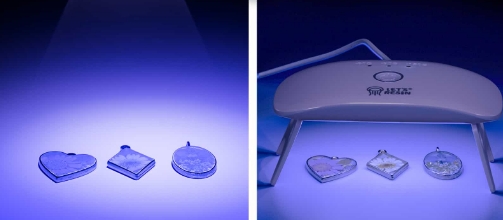
]]>How UV Flashlights Work for Resin Curing

Resin curing with UV flashlights is a process where ultraviolet light is used to initiate a chemical reaction in the resin. This reaction hardens the resin, allowing it to maintain its shape and structural integrity.
- Photoinitiators: Special chemicals in UV resin that react when exposed to UV light, causing the resin to polymerize and harden.
- Polymerization: The process in which the liquid resin transforms into a solid, durable form due to UV light exposure.
For optimal curing results, the UV light should have the correct wavelength, intensity, and power output.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a UV Flashlight for Resin Curing
1. Wavelength
The wavelength of UV light plays a significant role in resin curing. UV flashlights typically emit light in the range of 365nm to 405nm.
- 365nm: This wavelength provides pure UV light and is considered ideal for curing resin, especially for deeper curing of thicker layers.
- 395nm: This wavelength emits UV light with a bit of visible light, and it’s useful for curing thinner layers of resin quickly.
| Wavelength | Best For |
|---|---|
| 365nm | Professional-grade resin curing, thicker layers. |
| 395nm | Faster curing for thinner layers, general DIY applications. |
2. Power (Wattage)
The power of a UV flashlight determines the intensity of the UV light, which directly affects the curing speed and effectiveness. Higher wattage provides more light and cures resin faster, but it may also cause uneven curing if the resin is too thick.
- Low Wattage (3W-5W): Ideal for small projects or thin layers of resin.
- High Wattage (5W-10W): Better for thicker resin layers or professional-grade applications that require faster curing.
| Power (Wattage) | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| 3W-5W | Ideal for general or DIY resin curing. |
| 5W-10W | Suitable for professional or industrial-grade curing. |
3. Battery Type
Resin curing projects often require prolonged use of UV light, so the type of battery is an important consideration.
- Rechargeable Batteries: Provide long-lasting power and are cost-effective in the long term.
- Disposable Batteries: Often lighter and more convenient for short, occasional use.
| Battery Type | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Rechargeable | Cost-effective, eco-friendly, and long-lasting. |
| Disposable | Convenient, ideal for quick tasks or when portability is crucial. |
4. Portability and Size
A compact and lightweight UV flashlight is important for ease of use and portability. Larger, heavier models may be less convenient for smaller projects or tasks that require frequent movement.
| Size | Best For |
|---|---|
| Compact | Ideal for small, portable use and DIY projects. |
| Large | Better for professional or industrial use where durability and longer runtime are needed. |
Top UV Flashlights for Resin Curing

Here is a list of some of the best UV flashlights for resin curing in 2025, with their key features and benefits:
1. TANK007 K9A5 UV Flashlight
Wavelength: 365nm
Power: 5W
Battery Type: USB Rechargeable
Best For: Professional resin curing, mineral identification, and pet stain detection.
- Key Features:
- Emits pure 365nm UV light for deeper resin curing.
- Portable and rechargeable for convenience.
- Durable aluminum alloy body with water resistance.
Why Choose It: The TANK007 K9A5 provides consistent UV output, ensuring efficient curing for thick resin layers, making it perfect for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
2. Convoy S2+ UV Flashlight
Wavelength: 365nm
Power: 3W
Battery Type: 18650 Rechargeable
Best For: General resin curing, hobbyist projects.
- Key Features:
- Compact design and rechargeable for ease of use.
- High UV output at 365nm for professional results.
- Excellent for curing small to medium resin projects.
Why Choose It: The Convoy S2+ is a budget-friendly yet powerful option for hobbyists, offering deep UV light penetration and consistent performance.
3. Nitecore CU6 UV Flashlight
Wavelength: 365nm / White Light
Power: 1000mW (UV)
Battery Type: CR123 or 18650 Rechargeable
Best For: Quick resin curing, surface applications.
- Key Features:
- Dual-function flashlight with UV and white light modes.
- Excellent for both UV resin curing and general tasks.
- Compact, durable, and suitable for fieldwork.
Why Choose It: The Nitecore CU6 is versatile, offering both UV and white light modes, making it ideal for various applications, including resin curing and everyday tasks.
4. Fenix TK25 UV
Wavelength: 365nm / White Light
Power: 1500mW (UV)
Battery Type: 18650 Rechargeable
Best For: Industrial applications, high-power curing.
- Key Features:
- Dual LED design with 365nm UV and white light options.
- Strong UV light for curing thicker resin layers quickly.
- Durable, high-performance flashlight for professional use.
Why Choose It: The Fenix TK25 UV is ideal for professional applications, providing deep UV light and versatility for various types of resin curing.
5. UV Beast V3
Wavelength: 365nm
Power: 3000mW
Battery Type: 2 x 18650 Rechargeable
Best For: Large-scale industrial applications.
- Key Features:
- Extreme UV output (3000mW) for fast curing of thick resin layers.
- Rugged design, perfect for industrial and professional settings.
- Wide beam for faster coverage and efficiency.
Why Choose It: The UV Beast V3 is perfect for high-demand resin curing applications, offering maximum power and fast results for large projects.
How to Choose the Best UV Flashlight for Resin Curing

When selecting the best UV flashlight for resin curing, consider the following factors:
- Wavelength: Choose a 365nm flashlight for deep curing of thick layers and a 395nm flashlight for faster surface curing.
- Power: Higher wattage (5W and above) is ideal for professional applications or thicker resin layers.
- Portability: Choose compact models for DIY projects and larger ones for professional, industrial use.
- Battery Type: Rechargeable batteries are more eco-friendly and cost-effective for prolonged use.
Conclusion
Choosing the right UV flashlight for resin curing is essential for achieving high-quality results in your projects. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional, selecting the appropriate flashlight based on wavelength, power, and portability will help you achieve the perfect cure for your resin.
The post Best UV Flashlight for Resin Curing: A Detailed Guide appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post The Science Behind UV Flashlight for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>What is Resin Curing?
Resin curing refers to the process in which liquid resin is transformed into a hard, solid form. This transformation happens when a chemical reaction is triggered by UV light or heat, depending on the type of resin being used. UV resin curing is particularly popular because it offers quick and precise curing, which makes it ideal for applications that require detailed work.
- Photoinitiators: Special chemicals in UV resin that react when exposed to UV light, causing the resin to polymerize and harden.
- Polymerization: The process in which molecules in the resin bond together to form a solid structure.
How Does UV Flashlight Cure Resin?

Step 1: Exposure to UV Light
When UV resin is exposed to ultraviolet light, it reacts with photoinitiators within the resin. This initiates the polymerization process, where the molecules in the resin start bonding together to form a hardened material.
| Photoinitiator | Reaction Under UV Light |
|---|---|
| Benzoin ethers | Causes rapid curing, common in many UV resins. |
| Camphorquinone | Often used in dental applications, reacts with light to harden the resin. |
| Thioxanthone | Used in inks and coatings, leads to hardening when exposed to UV. |
UV light wavelength: For the resin curing process, the wavelength of the UV light typically ranges between 365nm and 405nm. Different wavelengths react with different photoinitiators, which makes selecting the right UV flashlight essential for optimal curing.
Step 2: Polymerization and Hardening
Once the resin is exposed to UV light, the photoinitiators trigger polymerization. This process causes the liquid resin to become hard and durable.
| Wavelength | Resin Curing Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| 365nm | Ideal for deeper curing, suitable for thick resins and professional applications. |
| 405nm | Good for surface curing and faster results, commonly used for thin layers of resin. |
Key Factors in UV Resin Curing with Flashlights
1. Wavelength of the UV Flashlight
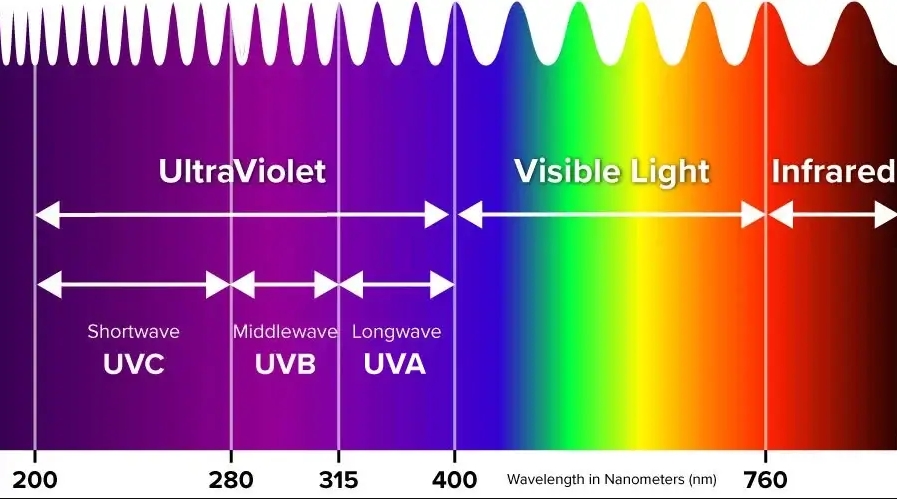
The wavelength of the UV flashlight plays a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of resin curing. Flashlights that emit a wavelength of 365nm provide a deeper and more intense curing effect, which is ideal for thick resin layers. 405nm wavelengths are effective for surface curing and are typically used for smaller or thinner resin projects.
- 365nm UV light: Best for curing deep layers and professional-grade resin applications. It provides better penetration into the resin.
- 405nm UV light: Typically used for curing thin layers of resin faster, suitable for DIY projects and small crafts.
| Wavelength | Depth of Curing | Best for |
|---|---|---|
| 365nm | Deeper penetration and longer curing time. | Professional-grade resin, deep applications. |
| 405nm | Surface curing with faster results. | Small-scale applications, quick-drying projects. |
2. UV Flashlight Power (Wattage)
The power output of a UV flashlight is another important factor. Higher wattage results in stronger UV light output, leading to faster curing. However, it is essential to balance power with resin thickness, as very high wattage can cause uneven curing if the resin is too thick.
| Wattage | Effect on Curing |
|---|---|
| 3W-5W | Suitable for general resin curing. |
| 5W-10W | Provides faster curing, ideal for professional use. |
| 10W+ | High power for quick curing of thicker resin layers. |
3. Exposure Time
The curing time depends on several factors, including the type of resin, the UV light intensity, and the resin’s thickness. Generally, thicker resins require longer exposure to UV light. Most UV resins will cure within a few minutes to an hour, depending on these factors.
| Resin Thickness | Exposure Time (at 365nm) |
|---|---|
| Thin Layer | 1-3 minutes |
| Medium Layer | 5-10 minutes |
| Thick Layer | 20-60 minutes |
Advantages of Using UV Flashlight for Resin Curing
- Speed: UV curing can occur in just a few minutes, unlike traditional curing methods that may take hours.
- Precision: With a UV flashlight, you can focus light on specific areas, ensuring precise curing without affecting surrounding surfaces.
- Convenience: Portable and easy to use, making it ideal for small-scale or DIY projects.
- Energy Efficient: UV flashlights consume less power compared to traditional curing ovens, which is especially beneficial for smaller workshops.
How to Choose the Right UV Flashlight for Resin Curing
When selecting a UV flashlight for resin curing, here are some factors to consider:
| Factor | What to Consider |
|---|---|
| Wavelength | Choose 365nm for deeper curing and 405nm for faster surface curing. |
| Power | Higher wattage (5W+) for quicker curing, lower wattage (3W) for precision. |
| Portability | Choose a compact, rechargeable flashlight for DIY or fieldwork. |
| Durability | Look for a flashlight with an aluminum body or impact-resistant design. |
Recommended UV Flashlight for Resin Curing: TANK007 K9A5
For efficient and high-quality resin curing, the TANK007 K9A5 UV Flashlight is a top choice. This flashlight offers:
- 365nm Wavelength: Provides optimal curing depth for a variety of resin types.
- Powerful 5W LED: Ensures fast and even curing for thick resin layers.
- Rechargeable Battery: Convenient and cost-effective, with long-lasting performance.
- Durable and Compact: Perfect for both professionals and hobbyists.
Conclusion
UV flashlights play a vital role in the resin curing process, enabling rapid and precise curing for a wide range of applications. By understanding the science behind UV curing, including the importance of wavelength, power, and exposure time, you can select the right flashlight for your resin projects.
The post The Science Behind UV Flashlight for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post Benefits of Using UV Flashlights for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>Why Use UV Flashlights for Resin Curing?
UV flashlights use ultraviolet light to cure UV-sensitive resin quickly and precisely. This process involves activating photoinitiators within the resin to harden it, offering a rapid and controlled method for small-scale or intricate projects.
Key Benefits of UV Flashlights for Resin Curing

1. Speed and Efficiency
- Rapid Curing: UV flashlights cure resin within seconds to minutes, depending on the layer thickness and resin type.
- Layered Application: Thin layers can be cured successively for a smooth, bubble-free finish.
2. Precision and Control
- Focused Beam: Allows for curing specific areas without affecting surrounding parts of the project.
- Adjustable Zoom: Many UV flashlights feature zoomable lenses for greater accuracy.
3. Portability
- Compact Design: Easy to carry and use anywhere, whether in a studio or on-site.
- Battery Operated: No need for a direct power supply, making it perfect for outdoor or mobile setups.
4. Cost-Effective Solution
- Affordable Entry Point: UV flashlights are generally less expensive than larger UV lamps.
- Durability: High-quality UV flashlights, like the Tank007 AA02, offer long-lasting performance.
5. Versatility
- Multiple Applications: Beyond resin curing, UV flashlights can be used for tasks such as detecting counterfeit currency, scorpion hunting, or mineral inspections.
Comparing UV Flashlights to UV Lamps

| Feature | UV Flashlight | UV Lamp |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Compact and portable. | Bulky and stationary. |
| Beam Control | Focused beam for precise curing. | Wider coverage, less precise. |
| Curing Speed | Slightly slower for large areas. | Faster for batch or large-scale projects. |
| Cost | Generally more affordable. | Higher initial investment. |
| Best Use Case | Small, intricate projects and portable needs. | Professional, large-scale, or batch projects. |
How to Maximize the Benefits of UV Flashlights
Choose the Right Wavelength
- 365nm: Ideal for professional-grade resin projects due to its pure UV output.
- 395nm: Suitable for hobbyist projects but may require longer curing times.
Use High-Quality Tools
The Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight is a top choice for resin curing with:
- 365nm wavelength for precise curing.
- 3W power output for fast and efficient results.
- Durable design for long-term use.
Follow Best Practices
- Cure in Layers: For thicker pieces, cure the resin in multiple thin layers to ensure even hardening.
- Avoid Overexposure: Excessive UV light can cause resin to yellow or crack.
- Use Safety Gear: Protect your eyes and skin from UV exposure with goggles and gloves.
Case Study: UV Flashlights in Action

Scenario: Crafting Resin Jewelry
A jewelry artist needed precise curing for intricate designs in resin pendants. Using the Tank007 AA02 UV flashlight, they achieved:
- Rapid Curing: Each pendant layer cured in under 30 seconds.
- Perfect Finish: Smooth, bubble-free surfaces due to layered curing.
- Increased Productivity: Ability to complete multiple pieces in a single session.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I use a 395nm UV flashlight for resin curing?
A: Yes, but 395nm flashlights may require longer exposure times and may not cure all resin types effectively.
Q: How do I know if my resin is UV-sensitive?
A: Check the manufacturer’s label; UV-sensitive resins are specifically designed to cure with ultraviolet light.
Q: Is a higher wattage always better?
A: Higher wattage often means faster curing, but ensure compatibility with your resin type to avoid overheating or overcuring.
Conclusion
UV flashlights are an indispensable tool for resin curing, offering unmatched speed, precision, and versatility. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, investing in a high-quality UV flashlight.
The post Benefits of Using UV Flashlights for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post Professional vs DIY Resin Curing with UV Flashlights appeared first on Tank007.
]]>Key Differences Between Professional and DIY Resin Curing
| Aspect | Professional Resin Curing | DIY Resin Curing |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment | High-grade UV flashlights with precise wavelength (e.g., 365nm). | Budget-friendly UV flashlights (often 395nm). |
| Applications | Commercial-grade projects like jewelry, coatings, and signage. | Hobbyist projects like small crafts, keychains, or repairs. |
| Curing Speed | Faster due to optimized tools and techniques. | Slower, especially with lower-powered flashlights. |
| Resin Types | Often uses industrial-grade UV-sensitive resin. | Commonly uses hobbyist-grade resin. |
| Results | Durable, professional finishes. | Satisfactory but may lack polish and longevity. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment. | Lower cost, accessible to beginners. |
| Skill Level | Requires expertise and experience. | Beginner-friendly with minimal learning curve. |
What Professionals Look For in a UV Flashlight

- Wavelength:
- 365nm UV flashlights are standard for professional curing, offering pure UV output for precise curing.
- Example: The Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight, designed for professional use, provides accurate and even curing.
- Power Output:
- High wattage (e.g., 3W or more) ensures faster and more efficient curing, ideal for large-scale or commercial projects.
- Durability:
- Sturdy materials and longer battery life ensure reliability during extended use.
Why DIY Enthusiasts Choose UV Flashlights
- Affordability:
- Budget-friendly options with wavelengths around 395nm are common for casual users.
- Ease of Use:
- Portable, battery-operated devices allow for flexibility in crafting spaces.
- Creative Freedom:
- DIYers enjoy experimenting with designs without worrying about commercial-grade perfection.
Comparison of Popular UV Flashlights
| Model | Wavelength | Power Output | Best For | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tank007 AA02 | 365nm | 3W | Professional resin curing. | $$ |
| Generic Budget UV Flashlight | 395nm | 1-2W | DIY projects and small crafts. | $ |
| Tank007 High Power NDT Flashlight | 365nm | 5W | Industrial and heavy-duty curing. | $$$ |
Key Considerations for Both Professionals and DIYers

- Resin Compatibility:
- Always ensure your resin is UV-sensitive and matches the flashlight’s wavelength.
- Layer Thickness:
- Thin layers cure faster and more evenly. For thick projects, use a step-by-step curing process.
- Safety Precautions:
- Wear UV-protective glasses and gloves to shield your eyes and skin from harmful UV exposure.
- Work Environment:
- Use in a controlled, low-light setting to enhance the UV light’s effectiveness.
Case Studies: Professional vs. DIY Projects
Professional Use: Jewelry Manufacturing
A jewelry artist used the Tank007 AA02 flashlight for curing intricate resin pendants. The 365nm wavelength ensured:
- Precise curing in under 30 seconds.
- A crystal-clear, bubble-free finish.
- Long-lasting durability, meeting commercial quality standards.
DIY Use: Home Decor Crafts
A hobbyist used a 395nm flashlight for crafting resin coasters. The process:
- Took longer (2-3 minutes per layer).
- Produced functional but less refined results.
- Was cost-effective and fun for personal projects.
When to Choose Professional vs. DIY Resin Curing

| Scenario | Recommended Approach | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Creating custom jewelry or signage. | Professional | Requires precision and a flawless finish. |
| Making gifts or personal crafts. | DIY | Cost-effective and adequate for casual use. |
| Scaling up for a business. | Professional | High efficiency and consistent quality needed. |
| Learning resin crafting as a hobby. | DIY | Beginner-friendly with minimal investment. |
Conclusion
Both professional and DIY resin curing with UV flashlights have their advantages. while DIYers enjoy the affordability and creativity of budget-friendly options.
By understanding your goals and the available tools, you can achieve the best outcomes for your resin curing projects. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a creative hobbyist, UV flashlights open up endless possibilities for innovation and artistry.
The post Professional vs DIY Resin Curing with UV Flashlights appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post FAQs About UV Flashlight for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>What Is a UV Flashlight, and How Does It Work?
A UV flashlight emits ultraviolet (UV) light, typically at wavelengths of 365nm or 395nm, which triggers a photochemical reaction in UV-sensitive resin, hardening it. This process is widely used in crafts, repairs, and small-scale projects due to its precision and convenience.
Why Is Wavelength Important in Resin Curing?
| Wavelength | Features | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| 365nm | Emits pure UV light, effectively curing most professional-grade UV resin. | Detailed and high-quality crafting, professional-grade projects. |
| 395nm | Emits a mix of UV and visible light; less effective for some resins. | Suitable for hobbyists or general-purpose crafting with less critical precision. |
What Are the Key Features to Look for in a UV Flashlight for Resin Curing?
| Feature | Why It Matters | Recommended Option |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | Determines compatibility with UV resin; 365nm is preferred for professional-grade results. | Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight |
| Power Output | Higher wattage ensures faster and more effective curing. | Opt for at least 3W flashlights for efficient curing. |
| Beam Focus | Adjustable focus allows targeted curing for small areas or wide coverage. | Zoomable lenses offer flexibility. |
| Battery Life | Long-lasting batteries reduce interruptions during projects. | Choose flashlights with rechargeable battery options. |
| Durability | Ensures longevity, especially for frequent use. | Aluminum casing with waterproof features is ideal. |
How Long Does It Take to Cure Resin with a UV Flashlight?

Curing time varies based on resin type, thickness, and UV flashlight power. Typically:
- Thin layers (<2mm): 10–30 seconds
- Thicker layers (>2mm): 1–2 minutes (curing in layers is recommended)
Can Any UV Flashlight Be Used for Resin Curing?
Not all UV flashlights are suitable for curing resin. For effective curing:
- Use a flashlight with a 365nm wavelength for best results.
- Ensure the flashlight has a minimum power output of 3W.
- Confirm compatibility with the resin type by checking the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Comparison: UV Flashlight vs. UV Lamp for Resin Curing
| Feature | UV Flashlight | UV Lamp |
|---|---|---|
| Portability | Compact and easy to carry. | Larger and stationary, ideal for workspace setups. |
| Beam Control | Adjustable focus for precise curing. | Covers a wider area but less precise. |
| Power Output | Typically lower than UV lamps, suitable for small projects. | High power for curing large or multiple items simultaneously. |
| Cost | Generally more affordable. | More expensive due to larger size and power output. |
| Best For | Hobbyists and small-scale projects. | Professional-grade or batch curing in studios or workshops. |
Are UV Flashlights Safe to Use?

Yes, but safety precautions are essential:
- Wear UV-blocking goggles to protect your eyes.
- Avoid direct exposure to skin.
- Keep the flashlight away from children.
- Store resin and tools in a shaded area to prevent unintended curing.
What Common Mistakes Should Be Avoided When Using UV Flashlights?
- Using the Wrong Wavelength: Always check the resin’s recommended wavelength.
- Overcuring: Excessive exposure can cause yellowing or cracks.
- Not Curing in Layers: Thick layers may not cure uniformly.
- Poor Flashlight Quality: Low-quality flashlights might not emit sufficient UV light.
How Does the Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight Enhance Resin Curing?
The Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight is designed with:
- 365nm wavelength for precise curing.
- 3W power output, ensuring fast and effective results.
- Durable aluminum body, ideal for frequent use.
- Compact design, perfect for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Conclusion
UV flashlights are indispensable for resin curing, offering unparalleled precision and versatility. By choosing the right flashlight and following best practices, you can create stunning resin art with ease. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned artist, the Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight is an excellent choice for all your resin crafting needs.
The post FAQs About UV Flashlight for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post Top Applications of UV Flashlights in Resin Art and Crafting appeared first on Tank007.
]]>How UV Flashlights Work in Resin Art

UV flashlights emit ultraviolet light, typically at wavelengths of 365nm or 395nm, to cure UV-sensitive resin. This process triggers a chemical reaction that solidifies the resin, providing strong, durable, and transparent results.
Top Applications of UV Flashlights in Resin Art

| Application | How It Works | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Small Resin Projects | Curing small items like charms, pendants, and beads with precision. | Quick curing and high accuracy for intricate designs. |
| Layered Resin Art | Curing each layer of resin individually to create depth and detail. | Allows control over complex, multi-layered projects. |
| Spot Repairs | Fixing imperfections, bubbles, or uneven surfaces in resin work. | Easy and efficient way to perfect your projects. |
| Embedding Objects | Securing small items like flowers, shells, or beads inside resin. | Prevents movement and ensures proper placement of embedded objects. |
| UV Resin Painting | Using UV resin to create textured art pieces or add highlights to existing art. | Versatile application for creative expression. |
Key Features to Look for in a UV Flashlight for Resin Art
| Feature | Why It Matters | Recommended Option |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 365nm is ideal for professional-grade curing; 395nm is suitable for general crafting. | Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight offers a precise 365nm wavelength. |
| Power Output | Higher wattage ensures faster and more effective curing. | A flashlight with 3W or above is highly recommended. |
| Beam Focus | Adjustable focus helps target specific areas or provide wide coverage. | Flashlights with zoomable lenses offer added flexibility. |
| Battery Life | Long-lasting or rechargeable batteries are more convenient for extended use. | Consider models that support AA or 18650 batteries. |
| Durability | Sturdy and heat-resistant materials ensure longevity and safe operation. | Look for aluminum casing with waterproof features. |
Comparison of 365nm vs. 395nm UV Flashlights in Resin Art

| Feature | 365nm UV Flashlight | 395nm UV Flashlight |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength Purity | Emits true UV light, better for professional-grade resin projects. | Emits a mix of UV and visible light, which may cause slight discoloration. |
| Curing Speed | Faster and more precise curing for UV resin. | Slightly slower, suitable for beginners or hobbyists. |
| Applications | Ideal for detailed and high-quality projects requiring flawless finishes. | Suitable for basic resin crafting and casual use. |
| Price Range | Slightly higher due to advanced features and wavelength accuracy. | Generally more affordable and widely available. |
Tips for Using UV Flashlights in Resin Art
- Wear Protective Gear: UV light can harm skin and eyes; use gloves and UV-blocking goggles.
- Use High-Quality Resin: Ensure the resin is UV-sensitive and compatible with your flashlight.
- Cure in Layers: For deep projects, cure in thin layers to avoid bubbles or uneven curing.
- Avoid Overexposure: Excessive UV light may cause resin to yellow or crack.
- Test Before Final Curing: Use the flashlight on a small area to ensure proper curing.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

- Using the Wrong Wavelength: A 395nm flashlight might not work effectively with some resins. Always check the resin’s specifications.
- Curing Too Quickly: Gradual curing ensures durability and reduces bubbles.
- Improper Storage of Resin: UV resin should be stored in dark, cool places to prevent premature curing.
Conclusion
UV flashlights revolutionize resin art by offering precision, speed, and control. Whether you’re a professional artist or a hobbyist, investing in a high-quality flashlight, such as the Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight, will significantly enhance your crafting experience. By understanding the applications, features, and best practices, you can create stunning, durable resin art with ease.
The post Top Applications of UV Flashlights in Resin Art and Crafting appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post UV Lights for Resin Curing: 365nm vs 395nm Which is Better? appeared first on Tank007.
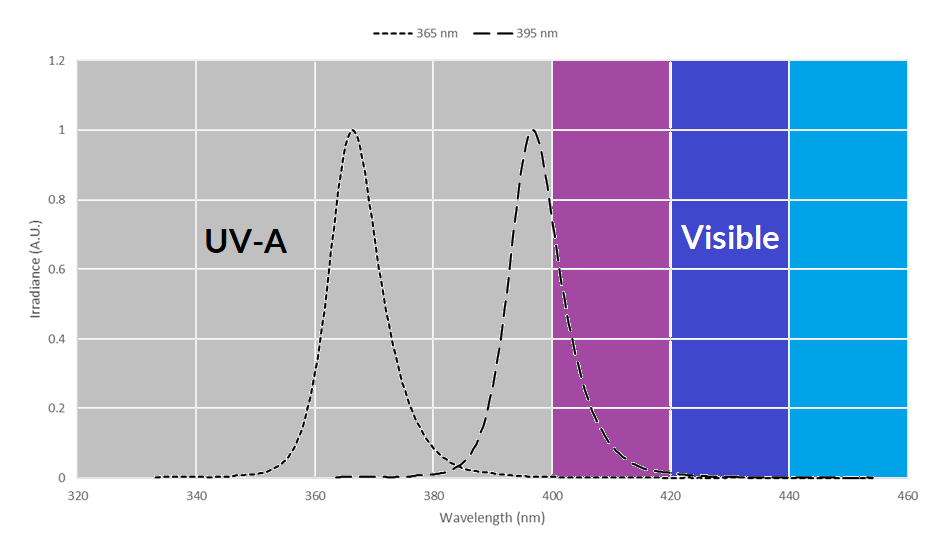
]]>Understanding UV Light and Resin Curing

UV light plays a key role in curing resin by initiating a photochemical reaction that hardens the material. The effectiveness of this process largely depends on the wavelength of the UV light used.
- 365nm UV light: Falls in the UVA spectrum, producing deeper and more precise curing.
- 395nm UV light: Also in the UVA spectrum but closer to visible light, offering slightly broader usability but less depth in curing.
Both wavelengths can cure resin, but choosing the right one depends on your project’s requirements.
Key Differences Between 365nm and 395nm UV Lights
| Feature | 365nm UV Light | 395nm UV Light |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 365 nanometers | 395 nanometers |
| Curing Depth | Deeper curing, ideal for thicker resins | Shallower curing, better for surface layers |
| Resin Compatibility | Works with most UV-curable resins | Works with resins less sensitive to UV light |
| Light Visibility | Low visibility (less visible to the naked eye) | High visibility (purple hue to the naked eye) |
| Heat Generation | Minimal heat during operation | Generates more heat |
| Power Consumption | Slightly higher due to precision | Lower power consumption |
| Applications | Professional-grade applications | General-purpose and hobbyist use |
| Cost | Typically more expensive | More affordable |
Benefits of 365nm UV Lights for Resin Curing
- High Precision: The shorter wavelength ensures more accurate and uniform curing, even in thicker resin layers.
- Deeper Penetration: Suitable for high-quality or professional resin projects.
- Minimal Yellowing: Prevents discoloration in clear resins, ensuring a clean finish.
Recommended Product: Tank007 AA02 UV Flashlight
- Features: High-power 365nm UV LED, professional-grade optical design, uniform light projection.
- Ideal For: Precision resin curing, mineral identification, and other professional applications.
- Learn More About AA02 Here
Benefits of 395nm UV Lights for Resin Curing

- Budget-Friendly: More affordable and widely available.
- Visible Light: Easier to see where the UV light is being applied.
- Good for Surface Curing: Works well for thin resin layers or quick fixes.
Choosing the Right UV Light for Your Project
When deciding between 365nm and 395nm UV lights, consider the following factors:
- Project Type: For professional applications or intricate designs, opt for a 365nm UV light. For general crafting or hobby projects, a 395nm UV light may suffice.
- Resin Thickness: Thicker resins benefit from the deeper penetration of 365nm UV lights.
- Budget: 395nm UV lights are a more economical choice for beginners or occasional use.
Practical Tips for Using UV Lights in Resin Curing

- Work in a Dark Environment: This minimizes interference from ambient light, ensuring optimal curing.
- Maintain Proper Distance: Keep the UV flashlight 2–5 inches from the resin surface for best results.
- Curing Time: Follow the resin manufacturer’s guidelines for exposure time, adjusting based on the UV light wavelength.
- Safety Precautions: Always wear UV-blocking glasses to protect your eyes from prolonged exposure.
Conclusion
Both 365nm and 395nm UV lights have their place in resin curing, but the best choice depends on your specific needs. If you’re aiming for professional-grade results or working with thicker resin layers, a 365nm UV light like the Tank007 AA02 is the ideal option. For general-purpose applications or budget-friendly solutions, 395nm UV lights can be effective.
By understanding the specifications and benefits of each wavelength, you can make an informed decision and achieve the best possible results in your resin curing projects. For premium-quality UV flashlights, explore our range at Tank007.
The post UV Lights for Resin Curing: 365nm vs 395nm Which is Better? appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post Top UV Lights for Resin Curing in 2025: A Complete Guide appeared first on Tank007.
]]>Why Choose UV Lights for Resin Curing?

UV lights offer a fast and effective way to cure UV resin, hardening it into a durable, glossy finish. Traditional curing methods, such as air-drying or using heat, can be time-consuming and less reliable. UV lights, on the other hand, provide a consistent and rapid curing process that allows resin artists to create intricate designs with precision.
Key benefits of using UV lights for resin curing include:
- Speed: UV curing is much faster compared to traditional methods, with most resins curing within minutes.
- Precision: UV lights offer controlled exposure to UV rays, ensuring that the resin cures evenly without bubbles or imperfections.
- Durability: UV-cured resin has a strong and glossy finish that is resistant to scratches and fading.
What to Look for in a UV Light for Resin Curing?

When choosing a UV light for resin curing, there are several factors to consider:
- Wavelength: The wavelength of the UV light determines how effectively it will cure the resin. Resin curing typically requires UV-A light (365 nm or 395 nm).
- Power Output: The power output, measured in watts, affects the intensity and curing speed. Higher wattage generally means faster curing times.
- Design and Size: UV lights come in various designs, from handheld flashlights to larger curing lamps. Choose one based on your workspace and the size of your resin projects.
- Portability: For artists who work on the go, compact and rechargeable models are ideal.
- Durability: A good UV light should be durable enough to withstand frequent use, especially for resin crafters who may use the light for long hours.
Top UV Lights for Resin Curing in 2025
Below are some of the best UV lights for resin curing, with a special recommendation for the AA02 UV Light from Tank007, which offers excellent features at a competitive price.
1. Tank007 AA02 UV Light (365 nm, 3W)
Product Link: Tank007 AA02 UV Light
Features:
- Wavelength: 365 nm (ideal for resin curing)
- Power Output: 3W
- Design: Compact and portable, can be used as a handheld flashlight
- Battery: Rechargeable lithium battery
- Build Quality: Durable aluminum body, impact-resistant
Pros:
- Small and portable, perfect for on-the-go artists
- High intensity UV light for fast and even curing
- Rechargeable, reducing the need for disposable batteries
- Affordable price point
Cons:
- Limited to small projects due to its size
- Requires close proximity to the resin for optimal curing

Why It’s Recommended:
The Tank007 AA02 UV Light is perfect for smaller resin crafting projects due to its portable size and strong UV output. It offers the convenience of rechargeable batteries, making it an eco-friendly choice. With a wavelength of 365 nm, it provides effective curing for most UV resins.
2. ArtResin UV Curing Lamp
Features:
- Wavelength: 395 nm (effective for a wide range of resins)
- Power Output: 36W
- Design: Large lamp with a broad curing surface
- Battery: Plug-in electric, no need for batteries
Pros:
- Large curing surface allows for curing multiple pieces at once
- Reliable and durable for heavy use
- Faster curing time due to high power output
Cons:
- Bulky and not portable
- Higher price point
Why It’s Recommended:
Ideal for serious resin artists with large projects, the ArtResin UV Curing Lamp offers a high-power output and expansive curing area. It’s a great choice for professionals who require consistent and fast curing.
3. UV LED Curing Lamp by Anycubic
Features:
- Wavelength: 405 nm (suitable for UV resins and 3D printing)
- Power Output: 48W
- Design: Compact with adjustable settings
- Battery: Plug-in electric
Pros:
- Multiple adjustable modes for different curing times
- Compatible with most UV resins
- Compact and easy to store
Cons:
- 405 nm wavelength may not be as effective as 365 nm for resin curing
- Requires proximity to the surface for best results
Why It’s Recommended:
This lamp is perfect for 3D printing resin curing and smaller DIY projects. Its adjustable settings make it versatile for various curing needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tank007 AA02 UV Light | ArtResin UV Curing Lamp | Anycubic UV LED Curing Lamp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 365 nm | 395 nm | 405 nm |
| Power Output | 3W | 36W | 48W |
| Design | Handheld, compact | Large, stationary | Compact, adjustable settings |
| Battery | Rechargeable lithium | Plug-in electric | Plug-in electric |
| Portability | High | Low | Medium |
| Curing Surface Area | Small | Large | Medium |
| Ideal for | Small projects | Large projects | 3D printing and small projects |
| Price Range | Budget-friendly | High-end | Mid-range |
Final Thoughts
When choosing a UV light for resin curing, it’s essential to match the tool to your project size and your budget. The Tank007 AA02 UV Light is a fantastic choice for hobbyists and smaller-scale resin projects due to its portability, high output, and affordability. For those working on larger pieces or requiring faster curing, the ArtResin UV Curing Lamp offers more power and a larger curing surface. Ultimately, your choice depends on your needs, workspace, and whether portability or power is more important.
Whichever UV light you choose, ensure that it matches the resin you’re using and the scale of your crafting projects. Happy crafting and curing!
The post Top UV Lights for Resin Curing in 2025: A Complete Guide appeared first on Tank007.
]]>The post Step-by-Step Guide to Using UV Flashlight for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>Introduction to UV Resin Curing
UV resin curing involves using ultraviolet light to initiate a photochemical reaction that hardens liquid resin into a solid form. This process is commonly used in crafting, jewelry making, coatings, adhesives, and electronics. Compared to traditional curing methods, UV curing offers faster results, greater control, and fewer environmental impacts.
Step-by-Step Guide to Curing Resin with a UV Flashlight
Step 1: Choose the Right UV Resin

Select a UV-curable resin compatible with your project. Make sure to choose high-quality resin that matches the desired hardness, clarity, and curing time for your application.
Key Considerations:
- Low-viscosity resins are suitable for intricate molds or small details.
- High-viscosity resins work well for thick layers or larger pieces.
- Ensure the resin specifies UV curing compatibility.
Step 2: Prepare Your Workspace
Set up a clean, dust-free, and well-ventilated workspace. Ensure all tools and materials are within reach. Use safety gear, such as gloves and safety goggles, to protect your skin and eyes from resin and UV light.
Step 3: Select the Right UV Flashlight

Choosing the correct UV flashlight is critical for effective curing. The key specifications include:
| Feature | Why It Matters | Recommended Range |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | Determines compatibility with the resin. | 365nm–405nm UV light |
| Light Intensity | Affects curing speed and efficiency. | 5W–12W for most resin applications |
| Beam Area | Helps target small or large curing areas. | Adjustable beam size preferred |
| Durability | Ensures long-term use without overheating. | Aluminum body, heat dissipation |
Step 4: Apply the Resin
Pour the resin into the desired mold or apply it directly onto the surface. Use a leveling tool or scraper to ensure even application. For multi-layered projects, apply thin layers of resin to ensure uniform curing.
Step 5: Start UV Curing
Hold the UV flashlight 1–2 inches away from the resin. Slowly move the flashlight across the surface to ensure even exposure to the UV light.
Tips for Curing:
- Thin Layers: Curing thin layers (1–2mm) provides the best results.
- Time: Curing times vary depending on the resin and flashlight intensity (typically 2–5 minutes per layer).
- Avoid Overheating: Take breaks if the flashlight or resin gets too hot.
Step 6: Check for Complete Curing

Inspect the resin for hardness and clarity after curing. If the resin feels tacky or soft, reapply the UV flashlight for another 1–2 minutes. For multi-layered projects, ensure each layer is fully cured before applying the next.
Step 7: Finishing Touches
After the resin has completely cured, remove it from the mold or clean the surface. Sand or polish the edges for a smooth finish, if necessary. Use a clear coat or additional UV resin for added shine or protection.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Resin remains tacky | Insufficient UV exposure | Increase curing time or use a stronger UV flashlight. |
| Uneven curing | Uneven resin application or exposure | Apply thinner layers and move the UV flashlight evenly. |
| Overheating of resin | Excessive UV exposure | Cure in shorter intervals and allow cooling time. |
Benefits of Using a UV Flashlight for Resin Curing
| Traditional Curing Methods | UV Flashlight Curing |
|---|---|
| Long curing times (hours to days) | Fast curing (minutes) |
| Requires heat or external equipment | Compact and portable flashlight |
| Limited precision | Greater control and targeting |
| High energy consumption | Energy-efficient and eco-friendly |
Conclusion
UV flashlights are essential tools for resin curing, enabling fast and efficient results for a wide range of applications. By following this step-by-step guide and using the right tools, you can achieve professional-quality results while minimizing common issues. With the right UV flashlight and techniques, resin curing becomes a seamless and enjoyable process.
The post Step-by-Step Guide to Using UV Flashlight for Resin Curing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>