The post Step-by-Step Guide to Using NDT UV Flashlights for Fluorescent Testing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) using UV flashlights plays a critical role in detecting surface and subsurface defects in industrial materials without causing damage. This guide provides a step-by-step process for effectively using NDT UV flashlights in fluorescent testing, highlighting best practices, safety measures, and technical details.
1. Understanding Fluorescent Testing in NDT
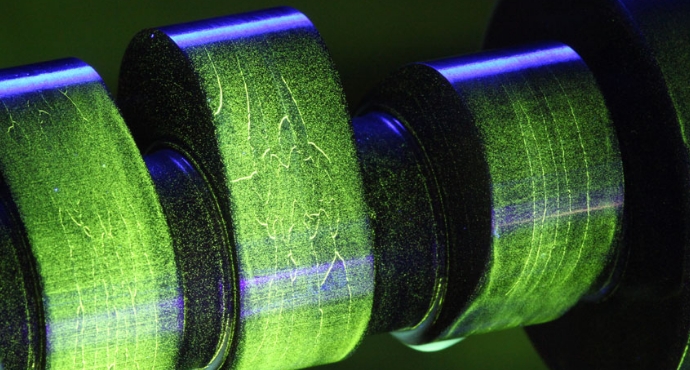
Fluorescent Testing is a method where materials are inspected under ultraviolet (UV) light after being coated with a fluorescent dye penetrant. When exposed to UV light, these dyes emit bright fluorescent colors, revealing cracks, fractures, or other defects.
Key Advantages:
- Non-invasive testing method.
- Accurate detection of surface and near-surface defects.
- Applicable in various industries (Aerospace, Automotive, Manufacturing).
2. Equipment Required for Fluorescent Testing
| Equipment | Description |
|---|---|
| NDT UV Flashlight | High-intensity UV light source (365 nm). |
| Fluorescent Dye Penetrant | Liquid dye for defect highlighting. |
| Cleaner/Remover | Removes excess penetrant. |
| Developer Spray | Enhances defect visibility. |
| Safety Gear | UV goggles, gloves, protective clothing. |
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Using NDT UV Flashlights
Step 1: Surface Preparation
- Objective: Ensure the surface is clean and free from contaminants.
- Actions:
- Use a cleaner to remove oil, grease, and dust.
- Ensure the surface is dry before applying the dye.
Step 2: Apply Fluorescent Dye Penetrant
- Objective: Allow the dye to penetrate surface defects.
- Actions:
- Evenly apply the fluorescent dye on the surface.
- Let it sit for the recommended dwell time (usually 10–30 minutes).
Step 3: Remove Excess Penetrant
- Objective: Avoid background fluorescence that could obscure results.
- Actions:
- Wipe off excess penetrant using a clean cloth.
- Avoid over-cleaning, as it may remove penetrant from defects.
Step 4: Apply Developer
- Objective: Draw penetrant from defects to the surface.
- Actions:
- Spray developer evenly over the surface.
- Allow sufficient time for the developer to act (5–10 minutes).
Step 5: UV Light Inspection
- Objective: Identify and evaluate defects under UV light.
- Actions:
- Darken the inspection area to reduce ambient light.
- Turn on the NDT UV flashlight (365 nm wavelength).
- Scan the surface systematically.
- Look for bright fluorescent indications that suggest cracks or defects.
Step 6: Record and Analyze Findings
- Objective: Document defects for reporting and analysis.
- Actions:
- Photograph and mark detected defects.
- Record the type, size, and location of each defect.
4. Comparison of NDT UV Flashlights vs. Standard Flashlights

| Feature | NDT UV Flashlight | Standard Flashlight |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 365 nm (optimal for NDT) | 400+ nm (ineffective) |
| Light Intensity | High-intensity UV output | General illumination |
| Fluorescence Detection | Yes | No |
| Application | Industrial inspections | General-purpose lighting |
5. Safety Precautions
- Always wear UV-blocking goggles to protect your eyes.
- Avoid direct skin exposure to UV light for prolonged periods.
- Ensure proper ventilation when using chemical penetrants.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for each piece of equipment.
6. Best Practices for Effective Fluorescent Testing
- Maintain consistent distance between the flashlight and the inspection surface.
- Ensure the UV flashlight has stable power output.
- Regularly calibrate UV equipment for accuracy.
- Use low ambient light conditions during inspections.
7. Real-World Application Example
Scenario: Aerospace Component Testing
- Component: Aircraft engine turbine blades
- Method: Fluorescent penetrant testing with NDT UV flashlight
- Findings: Micro-cracks detected on critical load-bearing areas
- Outcome: Defective parts replaced before critical failure
8. Conclusion
Using NDT UV flashlights for fluorescent testing is an essential and highly effective method for identifying surface and near-surface defects. By following this step-by-step guide, inspectors can ensure consistent results, improved safety, and higher reliability in their inspections.
Explore Tank007’s Range of NDT UV Flashlights for Precision Testing!
The post Step-by-Step Guide to Using NDT UV Flashlights for Fluorescent Testing appeared first on Tank007.
]]>